Dramatic examples of prison gerrymandering show the need for new districting practices in the Bayou State.
by Ginger Jackson-Gleich,
October 9, 2020
Local governments across Louisiana will engage in redistricting after the 2020 Census. When they do, they will once again face decisions about whether to bestow disproportionate political power upon people who live near correctional facilities. The last time this process unfolded (following the 2010 Census), numerous jurisdictions — including parishes (akin to counties), cities, and towns — formed districts that were highly distorted by prison and jail populations.
For example, Allen Parish gave people living in a district with a federal correctional complex twice as much political power as residents who lived in districts without such a facility. Moreover, because Louisiana has the second-highest incarceration rate in the world and more than a dozen state or federal prisons (as well as dozens of local jails), it is unsurprising that these kinds of power imbalances — the result of “prison gerrymandering” — occur in many places throughout the state.
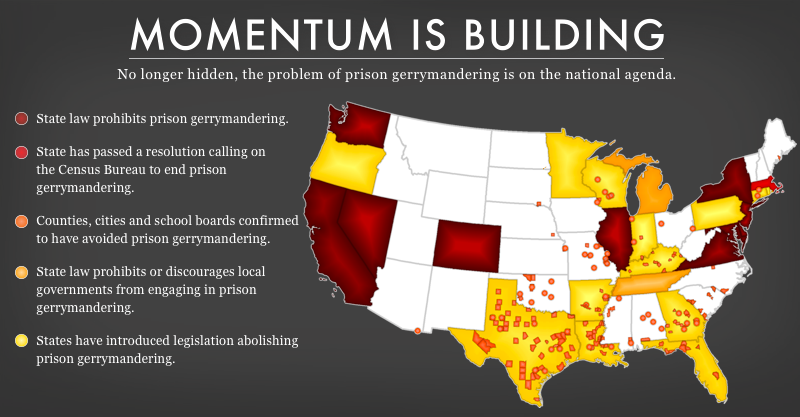
In addition to popping up in different parts of Louisiana, prison gerrymandering also occurs at numerous levels of government, creating problems at the state level (when district lines are drawn for state legislatures) and in parishes, cities, and towns where prison or jail populations typically constitute even larger portions of local district populations. In addition to undermining notions of representational equality, these population imbalances also create inaccurate pictures of community populations for research and planning purposes (although they do not typically impact federal funding, despite frequent assumptions to the contrary).
As we have explained before, prison gerrymandering happens primarily because the U.S. Census Bureau counts incarcerated people as residents of the places in which they are confined, despite the practical reality that (1) most people in prison cannot vote, and many people in jail are effectively barred from doing so (even if eligible), (2) most incarcerated people return to their home communities upon release and remain legal residents of their home addresses even while incarcerated, and (3) local elected officials often have little authority over the lives of people incarcerated within their districts.
While the state legislature in Louisiana engages in prison gerrymandering in drawing state districts, the state’s parishes (and the cities and towns within them) retain the power to utilize Census data to avoid prison gerrymandering when drawing local government districts. Indeed, as the Prison Policy Initiative has previously noted, some local governments in Louisiana have already taken it upon themselves to solve the problem of prison gerrymandering by removing incarcerated people from the districts they have drawn.
Notably, among the parishes with the largest prison populations (proportionally speaking), about half excluded prison populations during redistricting following the 2010 Census. For example, had Claiborne Parish included the prison population contained within its borders, one of the districts in the parish would have been composed entirely of a state prison.
Nonetheless, in many places throughout Louisiana, prison gerrymandering remains a problem. As noted above, Allen Parish is one striking example. The parish’s governing body (its police jury) has seven districts. According to the Census, Allen Parish had a total population of 25,764 in 2010; thus, each of the seven districts in its police jury should have had approximately 3,681 constituents following its 2010 redistricting.
However, Allen Parish relied on non-adjusted Census data to apportion people into those districts, and for one district (District 1) that data included 2,430 people incarcerated at the federal correctional complex within its borders. Using the raw Census data without adjusting it to account for the federal correctional complex meant that 66% of the “constituents” in District 1 ended up being people incarcerated at a federal prison, rather than people who would be meaningfully represented by the district’s elected police juror.
Examples from across the state show that the problem of prison gerrymandering looms large across Louisiana:
- Allen Parish:
- Police Jury District 1 (as explained above) includes the people incarcerated at the Oakdale Federal Correctional Complex, such that the incarcerated population accounts for 66% of the district’s “constituents.”
- Police Jury District 6 includes the people incarcerated at the Allen Correctional Center, such that the incarcerated population accounts for 39% of the district’s “constituents.”
- Madison Parish:
- Police Jury District 2 includes the people incarcerated at the Madison Parish Correctional Center, such that the incarcerated population accounts for 37% of the district’s “constituents.”
- Police Jury District 3 includes the people incarcerated at the Louisiana Transitional Center for Women, such that the incarcerated population accounts for 20% of the district’s “constituents.”
- Town of Farmerville
- District C includes the people incarcerated at a local detention center, such that the incarcerated population accounts for 42% of the district’s “constituents.”
Examples like these make clear that prison gerrymandering causes serious distortions to representational equality between constituents. In Allen Parish’s District 1, residents get twice the representation that residents of districts without a correctional facility have. Likewise, in Madison Parish’s District 2 (where the prison constitutes 37% percent of the population), every 63 residents in that district get the same degree of representation as 100 residents living elsewhere. Finally, in Farmerville, the jail in District C constitutes 42% of the district’s population, meaning that 58 residents there have the same political power as 100 residents elsewhere.
While the Census could solve the problem of prison gerrymandering in one fell swoop–by counting incarcerated people at home–it has so far declined to do so. In the absence of such a solution, states, counties, and local governments must act (as some Louisiana state legislators are already attempting to do).
Although it appears unlikely that Louisiana will count incarcerated people at home when drawing state legislative districts after the 2020 Census, cities and parishes can still avoid prison gerrymandering at the local level when they redistrict. Doing so will ensure that Louisiana residents have equal access to their parish, city, and town representatives and a fair say in local government.