A mid-decade opportunity to end prison gerrymandering in Michigan and Wisconsin
Courts in Michigan and Wisconsin have stuck down their legislative maps, providing a rare mid-decade opportunity to immediately end prison gerrymandering.
by Mike Wessler, January 17, 2024
While most people around the country were focused on the festivities of the holiday season, courts in two states — Michigan and Wisconsin — ordered them to redraw their legislative districts after they were ruled unconstitutional. This move provides each state with a rare opportunity to address prison gerrymandering in the middle of a decade, rather than waiting for the next Census.
Prison gerrymandering is a problem created by the Census Bureau. During its tally every decade, it erroneously counts incarcerated people as residents of prison cells, rather than in their home communities, artificially inflating the population of prison towns. When states then use this data to draw new legislative districts, areas that contain prisons get additional political clout, at the expense of everyone else.
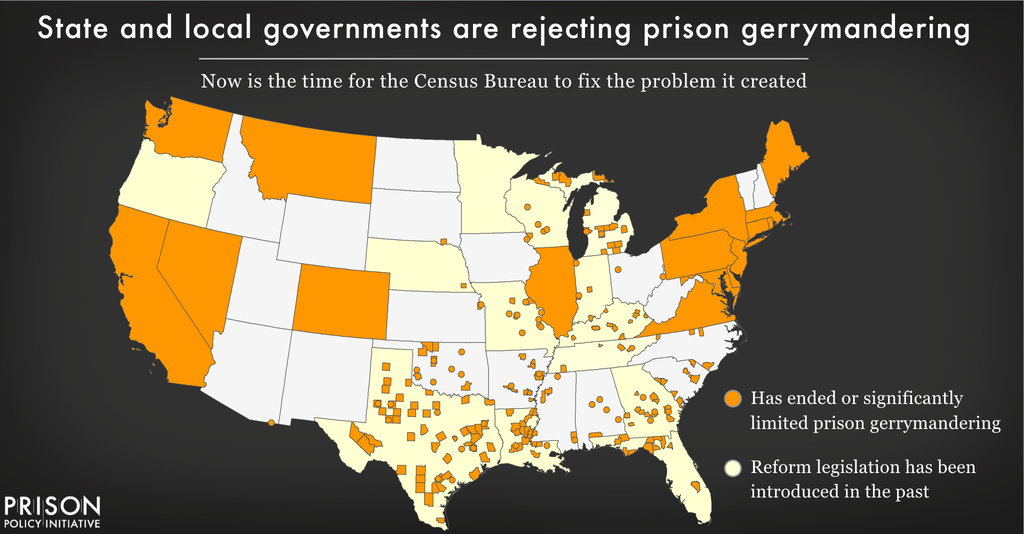
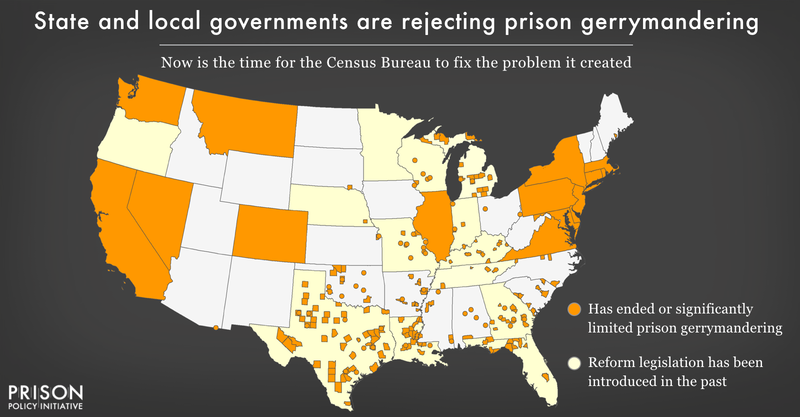
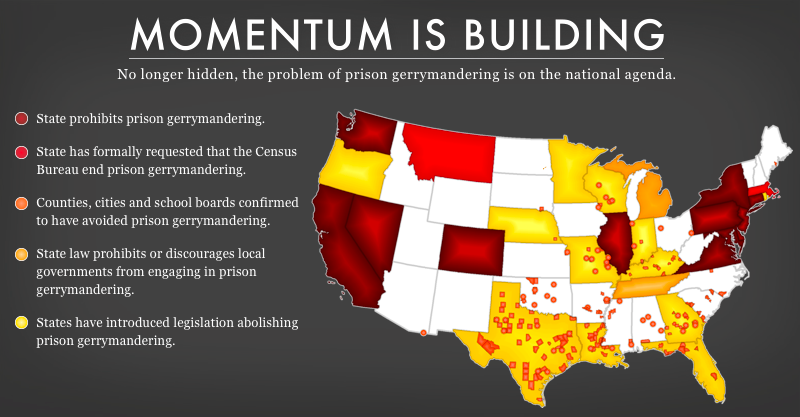
More than a dozen states have taken action to fix the Census Bureau’s error — including “red” states like Montana and “blue” states like California. Momentum on this issue has been so swift, in fact, that the fiercely bipartisan National Conference of State Legislatures recently called it “the fastest-growing trend in redistricting.” Roughly half the country now lives in a place that has addressed the problem.
The court-ordered redistricting in Michigan and Wisconsin gives each state a chance to join this growing movement, but they have to act fast.
Michigan’s chance to address racial disparities
In late December, federal judges ruled that 13 Detroit-area state legislative districts unfairly diluted the political clout of Black residents, and ordered the state’s independent redistricting commission to redraw them for the 2024 elections. Commissioners have until February 2 to produce new maps.
While the court only explicitly ordered that 13 districts be redrawn, changing the lines of these districts will almost certainly have statewide ripple effects.
Because the court ruling involved the dilution of Black representation, it is important to remember the disproportionate impact that prison gerrymandering has on Black residents in the state. Black residents are 13% of the state’s population but 51% of the people in state prisons. As a result of this disparity and the state’s failure to address prison gerrymandering, Black political representation across Michigan is being unfairly diluted.
As the redistricting commission draws new districts, it should address prison gerrymandering to return some political clout to Black communities in the state. In addition, the legislature should adopt Sen. Sylvia Santana’s bill to end prison gerrymandering in the state permanently. The state already prohibits prison gerrymandering in local government districts; ending it in state legislative districts is the next logical step.
Wisconsin’s opportunity to draw more fair districts
The day after Michigan’s districts were struck down, the state Supreme Court in neighboring Wisconsin also struck down that state’s legislative maps. Wisconsin has long been considered one of the most politically gerrymandered states in the nation. This order provides an opportunity to draw fair Wisconsin maps for the first time in decades.
Addressing prison gerrymandering won’t solve all of the issues with Wisconsin’s current legislative districts, but it will be a meaningful step toward ensuring fairer representation in the state.
For example, in Wisconsin’s Assembly District 53, roughly 8% of people counted in that district are incarcerated and live outside of that area. That means that 92 residents of that district have the same political sway as 100 residents in any other district that doesn’t have a prison. Ending prison gerrymandering will ensure that residents of this district don’t get a louder voice in government, simply because they live near a prison.
Recognizing that the governor and state legislature would be unlikely to reach a consensus on new maps, the court appointed two experts to review the submitted maps. They can then either alter the submissions or produce their own maps that resolve the court’s concerns. Notably, these experts have helped Virginia, Pennsylvania, and New York — three states that have addressed prison gerrymandering — draw their current legislative districts. Since these two experts already understand this issue and the ways to solve it, the final maps they propose should address prison gerrymandering to the fullest extent possible.
Failure to act means at least eight more years of prison gerrymandering
Redistricting officials in these two states have a lot of work ahead of them, and not much time to do it in. Ending prison gerrymandering in the state should be near the top of their list of priorities.
We’re hopeful that the Census Bureau will fix its prison gerrymandering mistake in the 2030 count. But Michigan and Wisconsin don’t have to wait that long to fix their prison gerrymandering problem. They have an opportunity to end prison gerrymandering while addressing problems with their state legislative maps right now. They should take advantage of it.