Federal Court Rules that Prison-based Gerrymandering Violates the Constitution
A U.S. District Judge ruled today that the City of Cranston violated the one person, one vote principle of the U.S. constitution when it counted people incarcerated at the Adult Correctional Institutions as "residents" of one Ward of the City.
May 24, 2016
City of Cranston, Rhode Island ordered to redraw district lines within 30 days
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE: Tuesday, May 24, 2016
Contact:
Steven Brown (ACLU of RI): 401 831-7171
Providence, RI. — In a precedent-setting ruling, U.S. District Judge Ronald Lagueux issued a decision today holding that the City of Cranston violated the one person, one vote requirements of the U.S. Constitution when it allocated the entire incarcerated population of the Adult Correctional Institutions (ACI) as “residents” of one ward of the City when it drew district lines for the City Council and School Committee following the 2010 Census. The ruling allows the City 30 days to present the Court with a new redistricting plan meeting constitutional requirements.
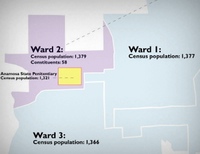
Today’s ruling, just the second of its kind in the nation, concluded that the City artificially inflated the population count of Ward 6, where the ACI is located, by treating all incarcerated persons as “residents” of the prison for redistricting purposes. Doing so, said the court, violates the rights of persons residing in other wards to equal representation as required by the Equal Protection Clause of the Constitution.
“I’m thrilled that our fight for equal representation has been successful,” said Karen Davidson, lead plaintiff. “Fairness in redistricting is a fundamental right and I’m glad that the court has vindicated our claims.”
At issue in the case was the City of Cranston’s choice to count the more than three thousand inmates at the ACI in a single city ward for the purposes of drawing City Council and School Committee districts. Plaintiffs argued this “prison gerrymandering” was improper because those incarcerated at the ACI are not true constituents of local elected officials, but instead remain residents of their pre-incarceration communities for virtually all legal purposes, including voting.
Judge Lagueux agreed with the plaintiffs’ claims, stating that “the ACI’s inmates lack a ‘representational nexus’ with the Cranston City Council and School Committee.” He noted that “Cranston’s elected officials do not campaign or endeavor to represent their ACI constituents,” and pointed out that that the majority of incarcerated persons cannot vote, and those who can are required by law to vote by absentee ballot from their pre-incarceration address.
Due to the questionable counting, persons at the only state-run correctional facility in Rhode Island account for 25% of Ward 6’s total “population.” According to Census Bureau data, without the incarcerated population, Ward 6 has only 10,209 true constituents. Yet those constituents now wield the same political power as the roughly 13,500 constituents in each of the other wards.
Cranston residents Karen Davidson, Debbie Flitman, Eugene Perry, and Sylvia Weber joined the ACLU of Rhode Island as plaintiffs in the case. They were represented in federal court by Demos, the Prison Policy Initiative, the American Civil Liberties Union, and the ACLU of Rhode Island.
“This is a big win for democracy,” said Adam Lioz of Demos, counsel for the plaintiffs. “Prison gerrymandering distorts representation and should no longer be tolerated. This decision should pave the way for other courts to address this long-standing problem.”
“We applaud the court’s decision requiring the City to correct its prison gerrymandering problem without delay,” said Steven Brown, executive director of the ACLU of Rhode Island. “It is time for Cranston to stop holding elections under a one-person, three-quarters of a vote regime.”
“Counting people at the ACI as constituents of Ward 6 officials made no sense,” said Aleks Kajstura of the Prison Policy Initiative. “They can’t use the park or library, attend a City Council meeting, or send their kids to public schools. And, even those who can vote must do so from their actual legal residence, not the prison location.”
“This ruling means that Cranston can no longer play games with our democracy by artificially inflating the political power of one district over another. People who are incarcerated should be counted as residents of the districts where they lived, not as so-called ‘residents’ of where they are involuntarily confined,” said Sean Young, staff attorney with the ACLU’s Voting Rights Project.
ACLU of RI volunteer attorney Lynette Labinger added: “The ACLU first urged the City to redraw its district lines four years ago in order to protect the rights of voters in the City’s five other wards. I am gratified that they should soon have their voices heard in equal measure with those in Ward 6.”
The case is Davidson et. al. v. City of Cranston. Plaintiffs’ complaint can be found here and their motion for summary judgment is here. Judge Lagueux’s ruling is here.



[…] See this press release from Prisoners of the […]