The Bureau is aware of our organizations' concerns about prison gerrymandering, but side-stepped our request to prioritize developing a solution.
by Peter Wagner,
May 17, 2013
Acting Director explains Bureau’s immediate priorities but sidesteps request to prioritize developing a solution to prison gerrymandering
The Census Bureau has replied to the February 14 letter from 210 organizations urging it to make “developing a methodology to tabulate incarcerated people at their home addresses a near-term priority.” I wanted to share the Census Bureau’s response, along with some of my thoughts about it. In a nutshell, the Bureau is aware of our organizations’ concerns about prison gerrymandering, but side-stepped our request to prioritize developing a solution.
Our coalition letter was intended to inform the Census Bureau that a diverse group of stakeholders wants the agency to start planning how to tabulate incarcerated people at home. In our view, the Bureau needs to recognize that the prison count is the largest and most visible failing with regard to where it tabulates people in the decennial enumeration, and start researching solutions now.
But in his reply to our letter, Acting Director Thomas Mesenbourg explained that the Bureau would not focus, in the near term, specifically on the issue of where the census tabulates incarcerated people. Instead, Mr. Mesenbourg described how researching solutions to prison gerrymandering fits into the Bureau’s current longer-term agenda: as one part of a much broader inquiry on residence rules that will take place — budget permitting — in Fiscal Year 2015. That falls far short of what we asked for, but the clarity of the Bureau’s response is helpful in determining our next steps. I wanted to share some further thoughts about the Acting Director’s letter, and some ideas moving forward.
The Bureau’s immediate priorities
The reply letter nicely summarizes the overall challenges the Bureau faces to maintain the quality of the decennial census while controlling costs, listing the four areas where the Bureau is currently focusing its energy. The Bureau then gives an update on an important moving target: exactly when research on improving the group quarters count could take place.
The problem of prison gerrymandering may be one of the most glaring defects in the Census, but, as the reply letter explains, the Bureau is instead prioritizing work on fundamental changes in the structure and operations of the decennial census in order to trim several billion dollars from the cost. I can see how the Census Bureau might, in contrast, view improving the tabulation of just one group of people — no matter how glaring the problem — as a lower priority.
The strategic challenge for our movement is not the complexity of the research required, it is the timing. Improving how incarcerated people are counted is not rocket science, but it does requires diligent planning. After all, people in prisons and jails are the only population in the country that the government counts multiple times every day. The Bureau needs sufficient time to find solutions to legitimate questions about the best way to collect and process these data.
In the reply letter, the Acting Director says that “research [on] other aspects” of the 2020 Census can begin only after the “high-level design” is completed, in 2015. This delay is potentially, though not definitively, problematic for the efforts to end prison gerrymandering by the next redistricting cycle. 2015 isn’t necessarily too late to begin researching how to tabulate incarcerated people at home in 2020, but it leaves a very small window of opportunity because the details of the 2020 Census will be locked in place long before 2020 rolls around. Unless the Bureau articulates a clear intent to pursue methods to tabulate incarcerated people at their homes of record, the passage of time will leave the Bureau will no choice but to continue its outdated methodology in the 2020 Census.
No clear statement on research priorities
While our letter acknowledged the Bureau’s budgetary challenges, our letter asked the Bureau to include ending prison gerrymandering in its near-term priorities. Unfortunately, the reply did not address the matter of priorities directly or explain why the Bureau can’t begin the process of planning improved ways to tabulate incarcerated people while it completes redesigning other components of the Census. Supporters of the constitutional principle of “One Person, One Vote” should be very concerned by the prospect of relegating the question of how incarcerated people are counted — the most visible fairness flaw in the decennial census — to only one piece of a larger research question that will not start until 2015, budget permitting.
The Role of Congress and the Bureau’s fear of controversy
The Census Bureau has the power to end prison gerrymandering, and the letter’s summary of the Bureau’s residence rules methodology since the Census Act of 1790 supports our position that the Bureau has the authority to revise its methodology to keep pace with social and demographic change. The question of where to tabulate incarcerated people is clearly within the Bureau’s discretion, but, as the Acting Director noted, the Bureau looks to Congress before making any changes that could be vulnerable to criticism.
Unfortunately, this fear of political controversy may be leading the Census Bureau to prioritize the consequences of changing the residence rule over the consequences of the status quo for the health of our democracy. The Acting Director’s one nod to the rule’s larger implications for democracy is that “[w]e understand fully the major impact on different states as well as counties and municipalities … [during] redistricting if we considered changing the residence rule” (emphasis added). Ironically, the Bureau’s own commissioned experts at the National Research Council of The National Academies had no such problem acknowledging the need for change, noting the current rule’s detrimental impact on democracy. During last decade’s review of the residence rules, the expert panel concluded that “[t]he evidence of political inequities in redistricting that can arise due to the counting of prisoners at the prison location is compelling.”
Even as the Acting Director’s reply letter stating that the Bureau “must inform and try to ascertain the will of the Congress on such a major change” was in the mail to me, the Census Bureau received evidence of congressional concern about the Bureau’s current policy. On April 1, 2013, 18 members of Congress wrote to the Bureau about why properly tabulating incarcerated people is important to state and local governments. They wrote, “We… urge the Census Bureau to take the steps necessary to ensure that Census 2020 counts prisoners at their home addresses to assist state and local governments in accurately representing these populations.”
Finally, the Bureau’s concern that “major change … regarding apportionment” necessitates the assent of Congress is a red herring. Congressional apportionment is unlikely to be affected by tabulating incarcerated people at home because most people do not cross state lines when they are incarcerated.
Moving forward
But beyond congressional weigh-in, the Census Bureau wants to get the input of as many stakeholders as possible before making a change to where incarcerated populations are counted. That is yet another reason why the comparatively straightforward activity of improving where incarcerated people are tabulated needs to start sooner rather than later.
Finally, the Bureau’s reply is a good indication of how much work we have left to do to establish why it is necessary to change where incarcerated people are tabulated. The letter, in my view, both understates the impact of prison gerrymandering on local and state governments and undervalues the Bureau’s own significant efforts to help those local governments by producing the Advance Group Quarters Summary File. This file, which the Bureau produced for the first time ever in 2010, was incredibly helpful to many state and local governments that wanted to eliminate, minimize or at least consider avoiding the effects of prison gerrymandering.
The driving reason to address prison gerrymandering is its dramatic impact on state and local governments. It is easy to understand why the Census Bureau, as a federal agency, might prioritize questions of congressional apportionment over state legislative, and even county/municipal, redistricting. But congressional apportionment is not the primary concern because prison populations are rarely significant in determining a 700,000 person Congressional district. The real impact of prison gerrymandering is at the state legislative level and, especially, at the county/municipal level. The smaller the legislative district, the more likely it is that a single prison could make up a large part, or even an actual majority, of the district. Taken together, prison gerrymandering’s impact is pervasive, and the overwhelming majority of the nation will benefit in at least one way when the practice comes to an end. As general messaging point, our movement needs to ensure that the real reasons to end prison gerrymandering remain in focus.
Moving forward, it is imperative that the Census Bureau continue to hear from all of its stakeholders — at the federal, state and local levels — that now is the time to address the problem of prison gerrymandering in order to resolve the problem by 2020. We shouldn’t have to wait until 2030 to fix such an obvious flaw in the Census Bureau’s methodology that compromises state and local democracy around the nation.
A handful of communities avoid prison gerrymandering and redistricting.
by Aleks Kajstura,
May 16, 2013
We’ve been monitoring how counties and municipalities across the nation have addressed prison gerrymandering. We found that the vast majority of communities (over 200) with both a large correctional facility and a district form of government avoided prison gerrymandering.
The communities employ different techniques but they all lead to the same result: districts are drawn as if the Census Bureau had not counted the incarcerated population in that community. Some communities adjust the Census figures, some “overpopulate” the district with the prison, and some cut holes in the maps around the prison. But a handful of communities avoid prison gerrymandering by avoiding redistricting.
Communities can comply with the principle of “one person, one vote” without redistricting, if their population has not changed. For example, a city whose population hasn’t changed from one decade to another does not need to redistrict as long as the population within each district also remained equal.
We’ve discovered a number of places that have chosen not to redistrict because the only significant change in the total Census population is the correctional population:
- Robinson City, Illinois saw population growth in the 2010 Census as a result of annexing the Robinson Correctional Center. The city didn’t redistrict after the 2010 Census, and really doesn’t have to. The total Census population has radically changed, but the resident population is basically the same. The old districts, drawn before the Census allocated the prison to the city, continue to fairly distribute political power to the city’s residents.
- Post City, Texas had a total population change of 1672 (a 36% increase) between the 2000 and 2010 censuses. But the city didn’t include the incarcerated population at the federal Giles W. Dalby Correctional Institution in its redistricting data when it redrew the city council districts in 2001, so when the prison’s population expanded from 371 in the year 2000 to 1,995 by the 2010 census, Post’s districts remained equally apportioned.
- The Town of Enfield, Connecticut also excluded the incarcerated populations at the Robinson Correctional Institution, Willard-Cybulski Correctional Institution, and Enfield Correctional Institution when it redistricted in 2010. Then after the 2010 Census, Enfield concluded that there was no significant population change and did not redistrict.
- Karnes City, Texas had a 12% change in total population reported by the Census, but most of that was due to a decrease in the incarcerated population at the Karnes County Correctional Center. Not counting the incarnated population, the town only lost 196 actual residents.
- Pike County, Missouri kept their district lines the same when the 2010 Census revealed little change in population. The County’s districts remain unskewed by the prison population at Missouri’s Northeast Correction Center.
So while these communities technically didn’t redistrict after the 2010 Census, they have rejected the Census Bureau’s prison counts and avoided prison gerrymandering.
Now that most state and local redistricting efforts have come to a close, it's clear that this data has been central to our recent advocacy efforts.
by Peter Wagner and Aleks Kajstura,
May 16, 2013
Two years ago, working within a tight timeframe, the Census Bureau released a new data product that made huge progress towards helping state and local governments avoid prison gerrymandering: the Advance Group Quarters Summary File.
This data, which identified the census blocks that contain group quarters such as correctional facilities, was released early so that state and local redistricting bodies could choose to use this information to draw fair districts.
Now that most state and local redistricting efforts have come to a close, we thought it would be useful to give an overview of how central this data has been to our recent advocacy efforts:
To make the file easier to use, within hours of the file’s release we:
- Prepared an ESRI point shapefile and Google KML files with the entire database, and for the correctional blocks, included links to our database of annotations.
- Released a web version (google maps, and tables) of the correctional portions of the file.
To make the file more informative, we:
- Labeled 80% of the blocks by facility name and type. (We have labeled 94% of blocks containing more than 100 people in a correctional facility. The smaller halfway houses and other facilities are much harder to identify and less relevant in the redistricting context.)
- When Summary File 1 was available, developed a methodology to determine the race/ethnicity (9 combinations) of the correctional population in each block for all but 4 blocks and then made this data available online.
- Reported the gender and age (<18, 18-65, 65+) of the correctional population for each block.
- Reported how the Census Bureau classified the correctional facility subtype for 99% of the blocks.
To make the file more widely known, we:
- Sent out a press release to our mailing list the same day the Bureau made the data available. We received immediate confirmation and thanks from a number of redistricting experts, particularly those who work with county and municipal governments.
- Sent out approximately 3,000 individual letters to most of the county commissioners and city councilors in the nation who have both a district form of government and a large prison in their jurisdiction. Letters sent out before the file was available described how and when to get the Advanced Group Quarters Summary File, and most letters sent out after the file was available included the specific block level data relevant to their community. We also offered additional technical support on request. Despite our letter not asking for a response, we received a number of thank you calls. We also saw considerable traffic on our website related to the file.
To support users of the data file, we also:
- Had numerous conversations about using and interpreting the data, including to assist New York State with implementing their law against prison gerrymandering. As the Bureau expected, Maryland officials also found the data useful when they redistricted in accordance with their own law.
By planning ahead to make the the Advance Group Quarters Summary File available, the Census Bureau took a big step forward towards ending prison gerrymandering at a time when it was too late to tabulate incarcerated people at their home addresses in the 2010 Census. Now, though, with the 2020 Census seven years away, the Census Bureau can plan ahead and develop the methodology needed to ensure that the next census counts incarcerated people in the right spot: at home.
Right now, 68,913,691 people live in a state, county or municipality that has formally rejected prison-based gerrymandering.
by Peter Wagner,
May 16, 2013
Right now, 68,913,691 people live in a state, county or municipality that has formally rejected prison-based gerrymandering. When we first started working on prison-based gerrymandering, almost no one had heard of the problem. Today, more than one in five U.S. residents has been protected from it:
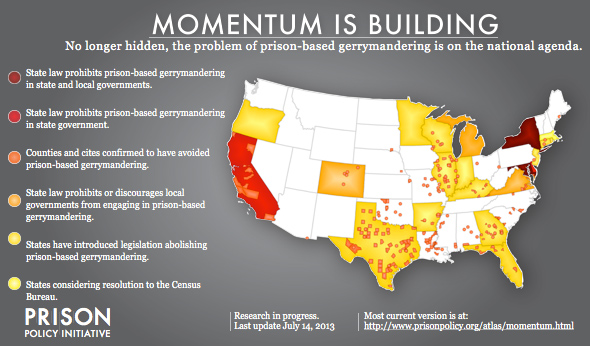
And yesterday the Illinois House passed HB 62 which would end prison gerrymandering in state legislative redistricting. Currently, 1.3 million people live in the 22 Illinois cities and counties reflected on our map that avoid prison gerrymandering in county or municipal redistricting. If HB 62 becomes law, we’ll update our map and be able to report that more than one in four people in the country — 26% — lives in a place that is protected from prison gerrymandering.
The bill now goes on to the Senate Assignments committee, where it needs to pass out within four days to go on to a Senate floor vote.
by Leah Sakala,
May 16, 2013
Yesterday afternoon the Illinois House passed HB 62, the “No Representation Without Population Act” to end prison gerrymandering! The bill now goes on to the Senate Assignments committee, where it needs to pass out within four days to go on to a Senate floor vote.
Illinois organizers on the ground are asking Illinois residents to please spread the word that a quick phone call urging your state Senator to join as a co-sponsor of the bill will help ensure that this bill will be successful in the Senate as well.
For some talking points or for more general information on prison gerrymandering in Illinois, please see our campaign page. We’ll be posting updates as soon as they’re available!

Ending prison gerrymandering is one of the report's 5 main recommendations to improve democracy in the Midwest.
by Leah Sakala,
May 14, 2013

This month the Midwest Democracy Network released a great new report, Redistricting and Representation in the Midwest, providing an overview of major democracy issues in Midwestern states and offering succinct recommendations on how to improve voting fairness.
The report calls for an end to prison gerrymandering as one of the five main recommendations (page 30):
The current practice of counting prisoners as residents in the district where the prison is located artificially inflates the representation of those districts and deflates representation in other districts.
The ultimate remedy is for the Census Bureau to count people where they are from rather than where they are incarcerated. Advocacy for this policy change prior to the 2020 count is underway.
In the meantime, the best option is for correction officials to track the home addresses of inmates and provide that information for use during redistricting in 2021. Delaware, Maryland, New York, and California have adopted legislation requiring use of home addresses of prisoners during state and local redistricting. The changes were in effect in the most recent round of redistricting in Maryland and New York, and will be applied after the 2020 Census in California and Delaware.
A possible compromise option is to exclude prison populations when drawing new district lines. The Census Bureau provides information needed for this step, and more than 150 local governments around the country, including Terre Haute, Indiana, address prison gerrymandering in this way. State laws that inhibit this local approach should be changed. Michigan, for example, adopted a state law that excludes prison populations in local government redistricting.
Our partners at the Midwest Democracy Network have been great leaders in the fight to end prison gerrymandering in the Midwest, including organizing a panel all about it at their most recent conference earlier this year. To stay in the loop about their important work, check out their website or Facebook, or follow them on Twitter.
Tom Condon wrote a wonderful column for today’s Hartford Courant on why it’s time for the Connecticut legislature to pass a bill ending prison gerrymandering.
by Leah Sakala,
May 9, 2013

Tom Condon wrote a wonderful column for today’s Hartford Courant on why it’s time for the Connecticut legislature to pass a bill ending prison gerrymandering. Here’s an excerpt (although the full piece is absolutely worth a read):
From the perspective of fairness and democracy, prisoners should be counted in their towns of residence. To see why, look at the Connecticut General Assembly in the early 1960s. State representatives were allocated by town — one for towns under 5,000 in population and two for towns with more than 5,000. So as my late and great friend Judge Robert Satter observed, the rural towns of Union and Hartland, with 1,440 residents between them, had the same number of representatives as did Hartford, which then had more than 162,000 souls. Thus, small rural towns could dominate large cities.
Such undemocratic malapportionment here and across the country led to the series of court cases espousing the “one man, one vote” rulings ordering that voting districts be apportioned on the basis of population — districts with roughly the same number of people.
But in Connecticut, most inmates cannot vote, and those who can — those who’ve not yet been sentenced or are in stir for a misdemeanor — must vote by absentee ballot in their towns of residence. So, we again have a form of malapportionment, what Peter Wagner of the Prison Policy Initiative calls “prison gerrymandering.”