Pennsylvania’s growing prison population distorts democracy
by Aleks Kajstura, October 16, 2009

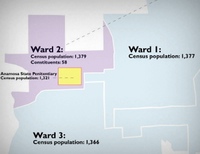
In Pennsylvania, there are eight state house districts that owe their existence to large prison populations in the 2000 Census. With the 2010 Census poised to count an even larger portion of the state behind bars, the prison count will be even more important.
The Census counts prisoners where they are incarcerated rather than where they legally reside. The Census figures are then used by states to draw district lines, apportioning voting power among their citizens. Regardless that the prisoners are not in any way connected to the community, they are counted in the local population making up the district. According to a recent article in Philadelphia’s The Legal Intelligencer, for example, State Rep. Bob Mensch, R-Montgomery, who represents District 147 with a population of 3,404 prisoners, has never gotten a single call from a prisoner.
Because the prisoners cannot vote but are credited to the prison district, their presence adds weight to every vote cast in the district. Such a system cannot be tolerated in a democracy. Indeed the Supreme Court barred practices such as this when it held, in Reynolds v. Sims, that: “The weight of a citizen’s vote cannot be made to depend on where he lives.” The Supreme Court ruled that the 14th Amendment’s equal protection clause required that districts be drawn to be substantially equal in population.
According to our recent research, the vote distortion created by the Census count is not randomly distributed throughout the state. For example, while only 12% percent of Pennsylvania’s population is in Philadelphia, 40% of Pennsylvania’s prisoners are from the city. And virtually all — 99% — are incarcerated outside of the city.
That temporary placement however, does not change where Philadelphia’s incarcerated citizens reside under state law. Like most states, Pennsylvania law says that a prison cell is not a residence. But the growing prison population and an outdated method of counting that population combine to threaten how political decisions are made. Until the Census changes where it counts people in prison, the state of Pennsylvania needs to change how it uses Census data.